
However, because kinetic energy is given by K = 1 2 m v 2 K = 1 2 m v 2, and velocity is a quantity that is different for every point on a rotating body about an axis, it makes sense to find a way to write kinetic energy in terms of the variable ω ω, which is the same for all points on a rigid rotating body. (credit: Zachary David Bell, US Navy)Įnergy in rotational motion is not a new form of energy rather, it is the energy associated with rotational motion, the same as kinetic energy in translational motion. However, most of this energy is in the form of rotational kinetic energy.įigure 10.17 The rotational kinetic energy of the grindstone is converted to heat, light, sound, and vibration. This system has considerable energy, some of it in the form of heat, light, sound, and vibration. Sparks are flying, and noise and vibration are generated as the grindstone does its work. Figure 10.17 shows an example of a very energetic rotating body: an electric grindstone propelled by a motor. However, we can make use of angular velocity-which is the same for the entire rigid body-to express the kinetic energy for a rotating object.
MOMENT OF INERTIA EQUATION FOR A HOLLOW SPHERE CALCULATOR HOW TO
We know how to calculate this for a body undergoing translational motion, but how about for a rigid body undergoing rotation? This might seem complicated because each point on the rigid body has a different velocity.

Rotational Kinetic EnergyĪny moving object has kinetic energy. With these properties defined, we will have two important tools we need for analyzing rotational dynamics. In this section, we define two new quantities that are helpful for analyzing properties of rotating objects: moment of inertia and rotational kinetic energy. So far in this chapter, we have been working with rotational kinematics: the description of motion for a rotating rigid body with a fixed axis of rotation. Calculate the angular velocity of a rotating system when there are energy losses due to nonconservative forces.Use conservation of mechanical energy to analyze systems undergoing both rotation and translation.Explain how the moment of inertia of rigid bodies affects their rotational kinetic energy.Define the physical concept of moment of inertia in terms of the mass distribution from the rotational axis.Describe the differences between rotational and translational kinetic energy.

Integrating from -L/2 to +L/2 from the center includes the entire rod.By the end of this section, you will be able to: Since the totallength L has mass M, then M/L is the proportion of mass to length and the masselement can be expressed as shown. To perform the integral, it is necessary to express eveything in the integral in terms of one variable, in this case the length variable r. The moment of inertia calculation for a uniform rod involves expressing any mass element in terms of a distanceelement dr along the rod. When the mass element dm is expressed in terms of a length element dr along the rod and the sum taken over the entire length, the integral takes the form: The general form for the moment of inertia is: The resulting infinite sum is called an integral. The moment of inertia of a point mass is given by I = mr 2, but the rod would have to be considered to be an infinite number of point masses, and each must be multiplied by the square of its distance from the axis. If the thickness is not negligible, then the expression for I of a cylinder about its end can be used.Ĭalculating the moment of inertia of a rod about its center of mass is a good example of the need for calculus to deal with the properties of continuous mass distributions. The moment of inertia about the end of the rod is The moment of inertia about the end of the rod can be calculated directly or obtained from the center of mass expression by use of the Parallel axis theorem. HyperPhysics***** Mechanics ***** Rotationįor a uniform rod with negligible thickness, the moment of inertia about its center of mass is This process leads to the expression for the moment of inertia of a point mass. This provides a setting for comparing linear and rotational quantities for the same system. If the mass is released from a horizontal orientation, it can be described either in terms of force and accleration with Newton's second law for linear motion, or as a pure rotation about the axis with Newton's second law for rotation.
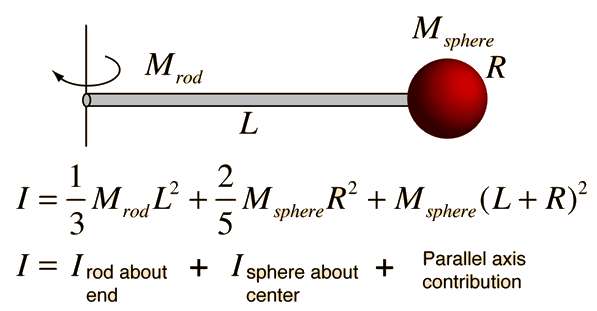
Moment of Inertia Rotational and Linear ExampleĪ mass m is placed on a rod of length r and negligible mass, and constrained to rotate about a fixed axis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
